Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is a fascinating cosmic structure full of wonders. Journey with us as we explore twelve amazing facts about our galactic home.
These insights not only highlight the grandeur of the Milky Way but also provide a glimpse into the mysteries of the universe.
1. Galactic Size

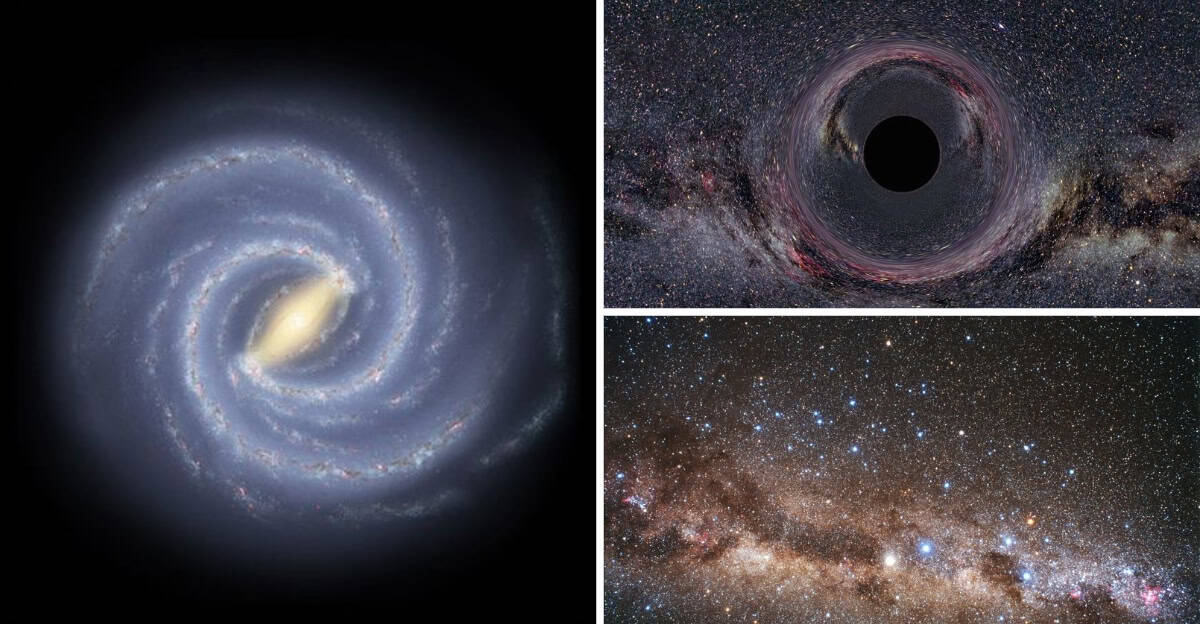
The Milky Way is an enormous barred spiral galaxy, spanning approximately 100,000 light-years in diameter.
Imagine a cosmic city bustling with stars, planets, and cosmic dust. This galactic giant holds hundreds of billions of stars within its spiral arms.
The sheer vastness of the Milky Way is mind-boggling, providing a cosmic playground for astronomers and space enthusiasts.
It’s a vast ocean of stars, each with its own secrets and stories, waiting to be discovered.
Our galaxy’s immense size showcases the incredible diversity and beauty of the universe.
2. Black Hole Center
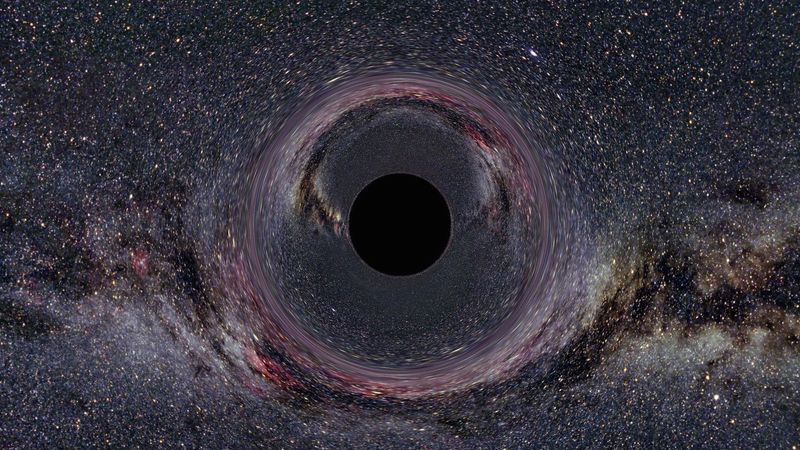

At the heart of the Milky Way lies a supermassive black hole named Sagittarius A*.
This cosmic monster has a mass equivalent to four million suns! Despite its colossal size, it remains invisible, exerting a powerful gravitational pull.
The black hole is surrounded by swirling stars and gas clouds, which it gradually consumes.
Its presence influences the entire galaxy, shaping its structure and dynamics. For scientists, Sagittarius A* is a window into the mysterious phenomena of black holes, offering insights into their formation and behavior.
3. Stellar Population

The Milky Way is a celestial metropolis, home to a diverse population of stars. From massive blue giants to smaller, cooler red dwarfs, each star contributes to the galaxy’s brilliance.
These stars are at different stages of their life cycles.
Our own Sun is just one of the many stars in this galactic collection. The diversity of stars offers a unique opportunity for studying stellar evolution and the life cycle of celestial bodies.
The Milky Way’s starry abundance is a testament to the complexity and wonder of our universe.
4. Dark Matter Halo
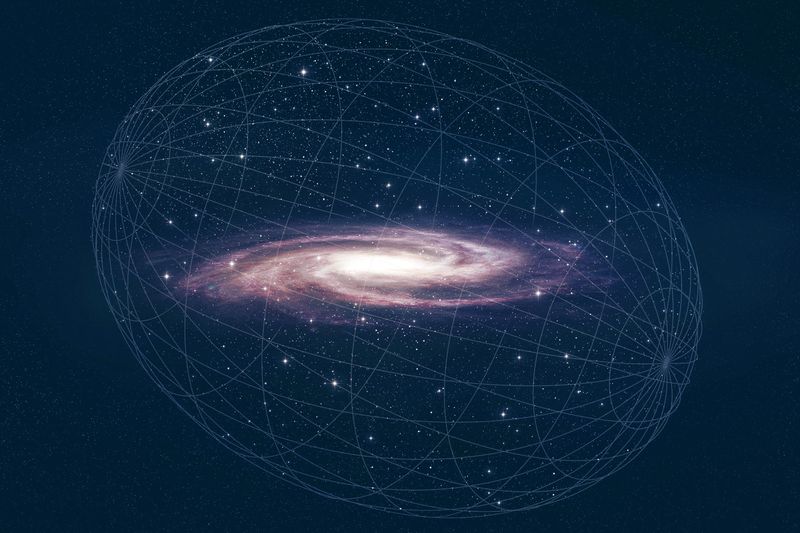

Surrounding the Milky Way, an unseen force called dark matter forms an extensive halo.
Though invisible, this mysterious substance exerts a gravitational pull, influencing the galaxy’s rotation and structure.
Dark matter accounts for most of the Milky Way’s mass.
Scientists are still unraveling the secrets of dark matter, which remains one of the universe’s biggest enigmas. Its presence is crucial for explaining gravitational effects that visible matter alone cannot.
Understanding dark matter is key to unlocking deeper cosmic mysteries.
5. The Galactic Halo
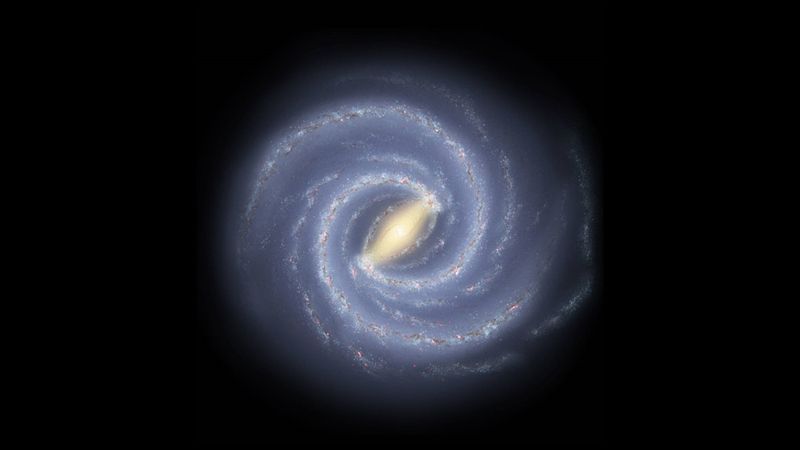

The Milky Way is encased in a halo of ancient stars and globular clusters. This spherical region extends beyond the visible galaxy, containing remnants from the early universe.
The halo’s stars are among the oldest in the galaxy.
These celestial fossils offer a glimpse into the Milky Way’s formative years, providing clues about its origin and evolution.
The galactic halo is a treasure trove for astronomers seeking to understand the Milky Way’s history and the broader cosmos.
6. Galactic Rotation
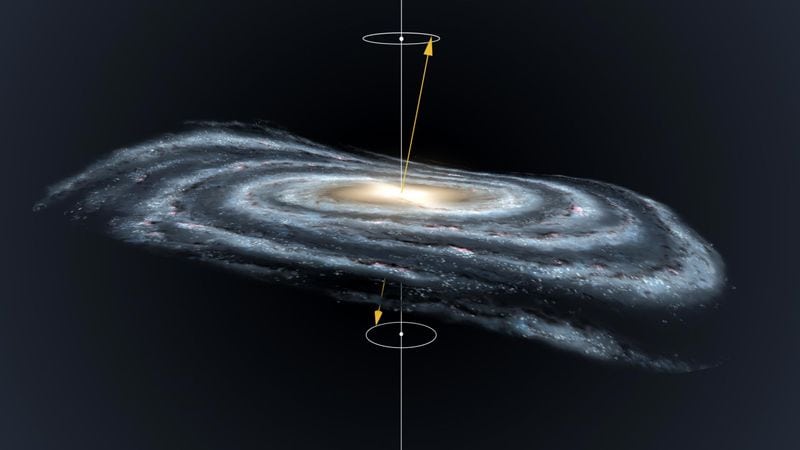
The Milky Way’s spiral arms rotate around the galactic center, driven by gravity. This rotation gives the galaxy its iconic spiral shape. However, not all parts of the galaxy rotate at the same speed.
The inner regions move faster than the outer ones, creating a dynamic and ever-changing structure.
Observing the Milky Way’s rotation helps scientists understand the distribution of mass within the galaxy.
It’s a fascinating dance of stars and celestial bodies, orchestrated by the forces of nature.
7. Interstellar Medium
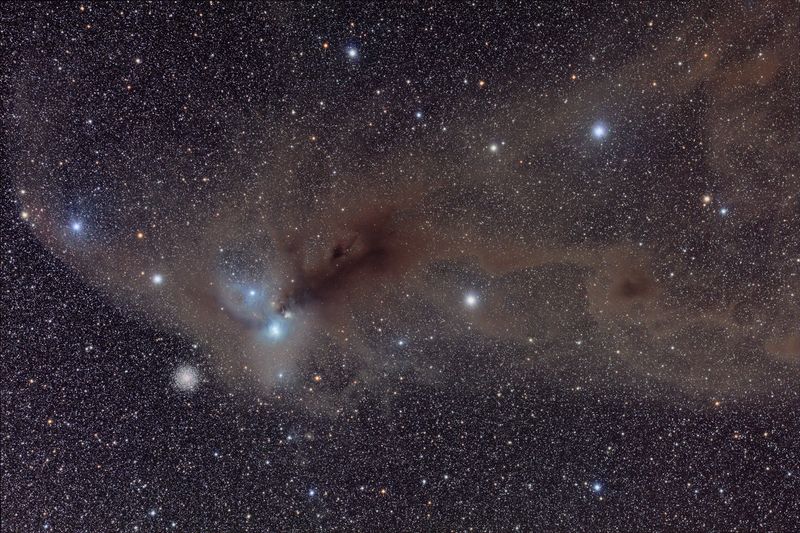

Between the stars of the Milky Way lies the interstellar medium, a vast expanse of gas and dust. This cosmic material serves as the raw ingredients for star formation, where new stars are born.
The interstellar medium is a dynamic and ever-changing environment, influenced by stellar winds and supernovae.
Studying this medium provides insights into how stars and planets are formed. It’s a reminder of the ongoing cycle of creation and destruction that shapes our galaxy.
8. Satellite Galaxies
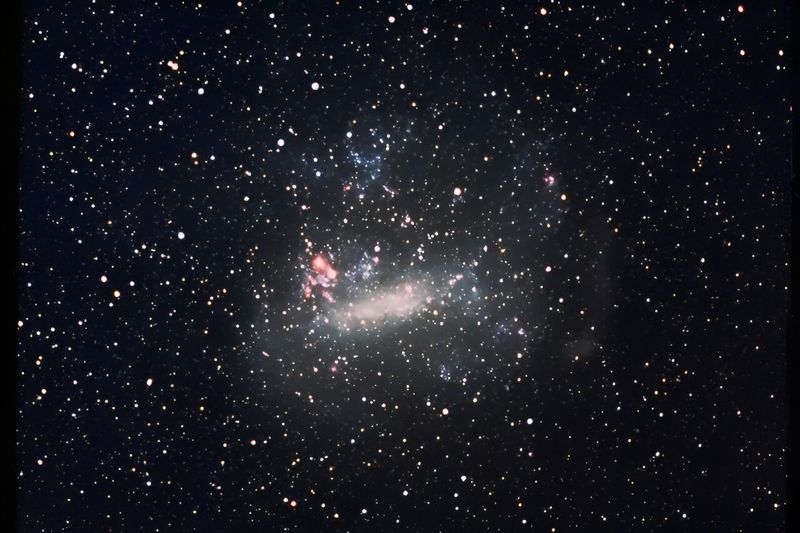

The Milky Way is not alone in the universe. It is accompanied by numerous smaller satellite galaxies, like the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. These galactic companions orbit the Milky Way.
Interactions with these satellites can influence the Milky Way’s structure and star formation.
Studying these galaxies helps astronomers understand galactic formation and evolution processes. The Milky Way’s cosmic neighborhood is a complex network of gravitational interactions.
9. Star Formation Regions
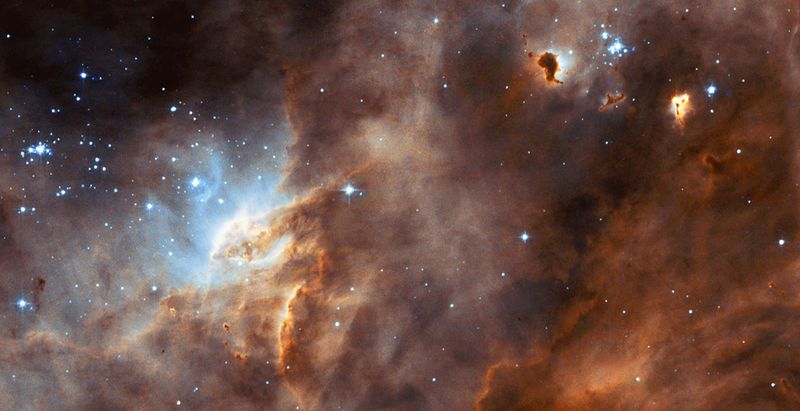

The Milky Way is dotted with star formation regions, where new stars are born from clouds of gas and dust.
These areas, like the Orion Nebula, are stellar nurseries glowing with young, hot stars.
The process of star formation is a complex and fascinating phenomenon, driven by gravity and nuclear fusion.
Observing these regions provides valuable information about how stars and planetary systems develop.
The Milky Way’s star formation regions are a testament to the dynamic nature of the universe.
10. Galactic Habitable Zone
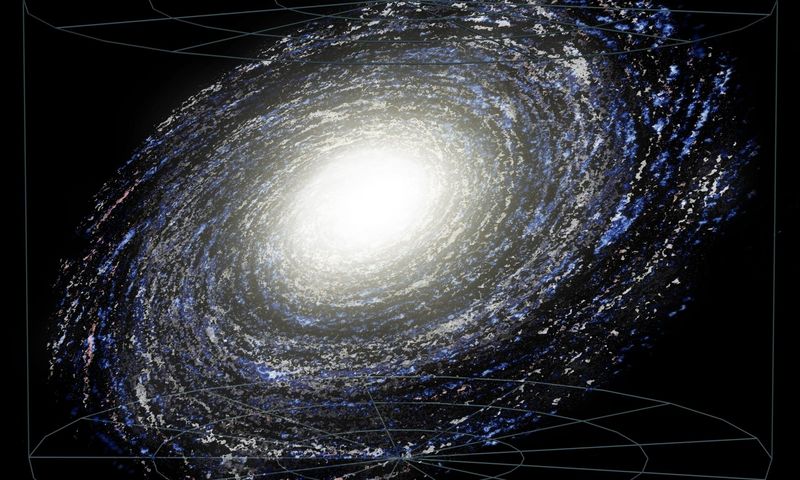
The Milky Way has a galactic habitable zone, a region where conditions may be suitable for life.
This zone is not too close to the galactic center, avoiding harmful radiation and gravitational forces.
Within this zone, stars with planets potentially harboring life could exist.
Understanding the galactic habitable zone aids in the search for extraterrestrial life. It’s a cosmic quest to answer one of humanity’s oldest questions: Are we alone in the universe?
11. The Sun’s Orbit
Our Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way, taking about 230 million years to complete one revolution. This long journey is known as a cosmic year or galactic year.
During this time, the solar system travels through different regions of the galaxy, influenced by various cosmic forces.
Understanding the Sun’s orbit provides insights into our solar system’s past and future locations. It’s a reminder of our place in the grand cosmic scheme.
12. Milky Way’s Future

In billions of years, the Milky Way is destined to collide with the Andromeda galaxy. This cosmic event will reshape both galaxies, forming a new elliptical galaxy.
While this collision may seem catastrophic, stars are unlikely to collide due to vast distances between them.
The event will trigger new star formation and reshape the cosmos.
Understanding such interactions helps scientists predict the Milky Way’s long-term future. It’s a glimpse into the ever-evolving nature of the universe.

