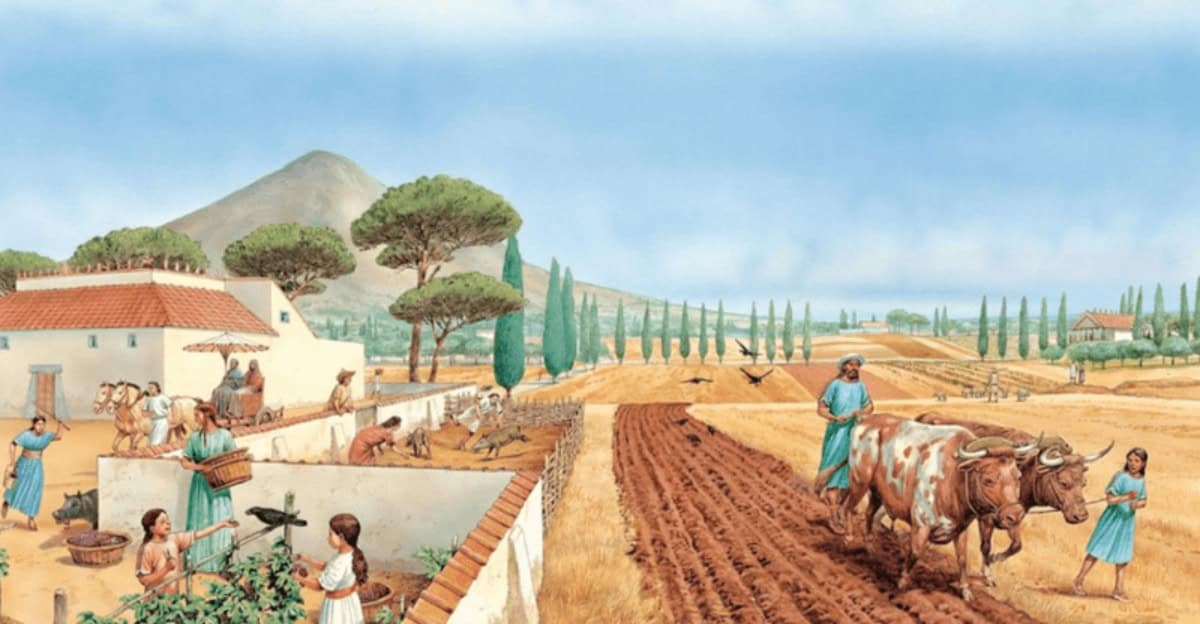
Exploring the fascinating world of ancient civilizations, we uncover common threads that defined their existence. Despite vast geographical distances and diverse cultures, these societies shared several core characteristics.
Dive into the seven elements that united these ancient peoples, and discover surprising facts about their world.
1. Agriculture
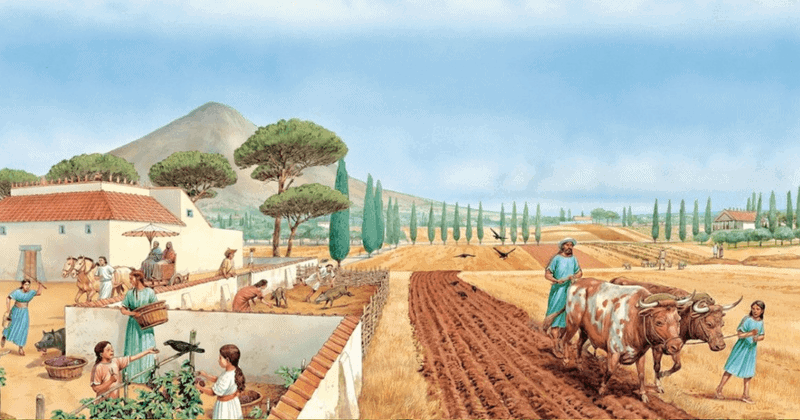
Agriculture was the backbone of ancient civilizations. By cultivating crops and domesticating animals, they ensured a steady food supply.
This development allowed them to settle in one place, leading to the growth of villages and cities. With agriculture, these societies could support larger populations and develop complex social structures.
It also led to innovations in tools and techniques, which further boosted productivity. Whether in the fertile crescent of Mesopotamia or the lush lands of the Nile, agriculture was key to sustainability and growth. It laid the foundation for trade, culture, and progress.
2. Religion and Beliefs
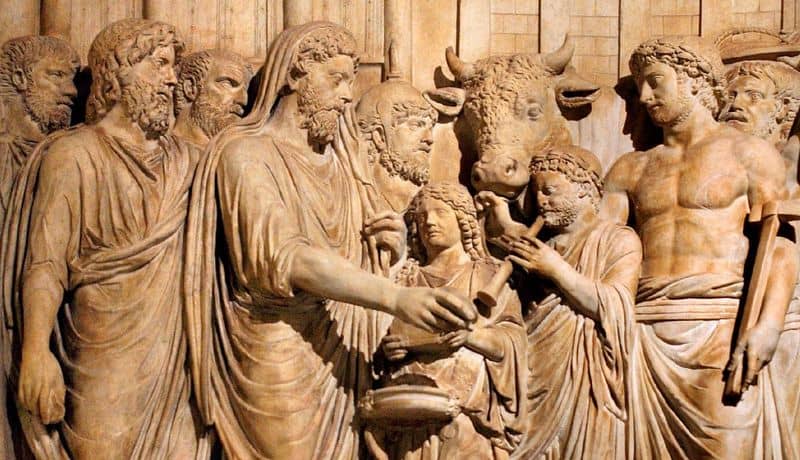

Religion played a vital role in uniting ancient societies. It provided a common belief system and moral code.
These beliefs often centered around natural phenomena, with gods and goddesses representing various elements. Temples and rituals were integral parts of daily life, acting as centers for social gatherings and cultural transmission.
However, religious leaders wielded significant power, influencing decisions and governance. This spiritual unity often strengthened social cohesion, providing meaning and purpose. From the majestic pyramids of Egypt to the enigmatic ziggurats of Mesopotamia, religion shaped architecture and art.
3. Trade Networks

Trade was the lifeline of ancient civilizations, connecting distant lands and cultures.
These networks facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, enriching societies. Markets bustled with activity as merchants traded spices, textiles, metals, and more.
Such exchanges promoted economic growth and cultural diffusion. They also helped forge diplomatic relationships between different regions. The Silk Road, for example, linked the East and West, leaving a lasting legacy of interconnectedness. Trade was not just about commerce; it was about exchange and interaction, shaping the world in profound ways.
4. Social Hierarchy
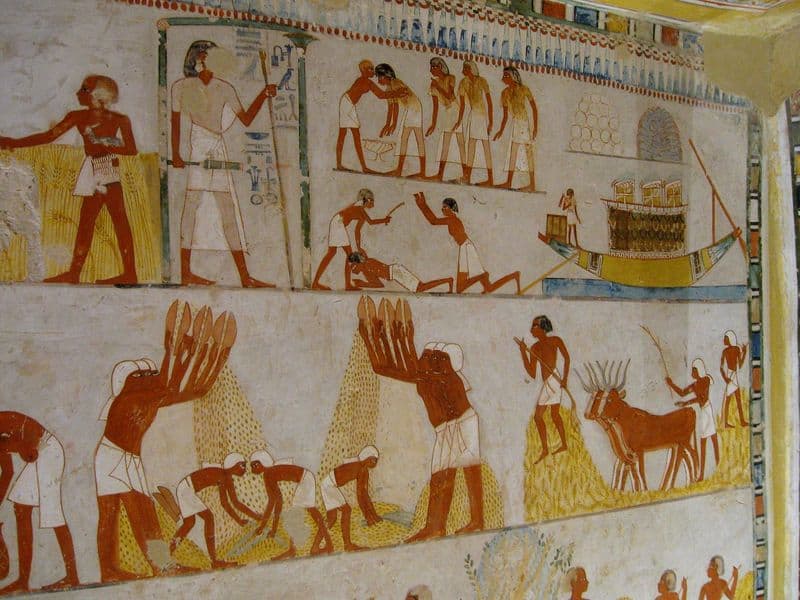

Social hierarchy was a defining feature of ancient civilizations. These societies were structured with clearly defined roles and classes.
From kings and priests at the top to slaves and laborers at the bottom, this hierarchy determined one’s duties and privileges. Such structures were often justified by religious or cultural beliefs, maintaining order and control.
Though rigid, these hierarchies allowed for some mobility through achievements or favor. They provided stability, ensuring that society functioned smoothly. However, they also led to inequality and exploitation, issues that resonate even today.
5. Writing Systems

Writing was a revolutionary development that transformed ancient civilizations. It enabled the recording of information, laws, and stories.
With writing, knowledge could be passed down generations, preserving history and culture. It facilitated administration and governance, allowing for organized societies.
Whether it’s cuneiform in Mesopotamia or hieroglyphs in Egypt, writing was crucial for communication and control. It empowered civilizations to document their achievements and challenges. This ability to record and transmit information was a cornerstone of progress and innovation.
6. Architecture and Construction
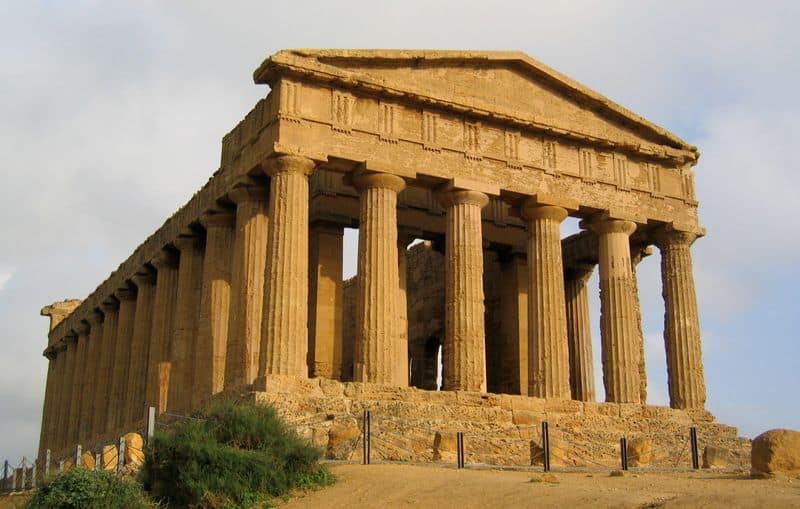

Architecture was a testament to the ingenuity of ancient civilizations. Through construction, they showcased their artistic and engineering prowess.
From the towering pyramids of Egypt to the intricate palaces of Persia, these structures symbolized power and belief. They required meticulous planning and skilled labor.
Such feats were possible due to advancements in mathematics and tools. These monumental works served religious, political, and social purposes, standing as enduring legacies. Architecture was not just about building; it was about making a statement, reflecting the values and aspirations of a society.
7. Law and Governance
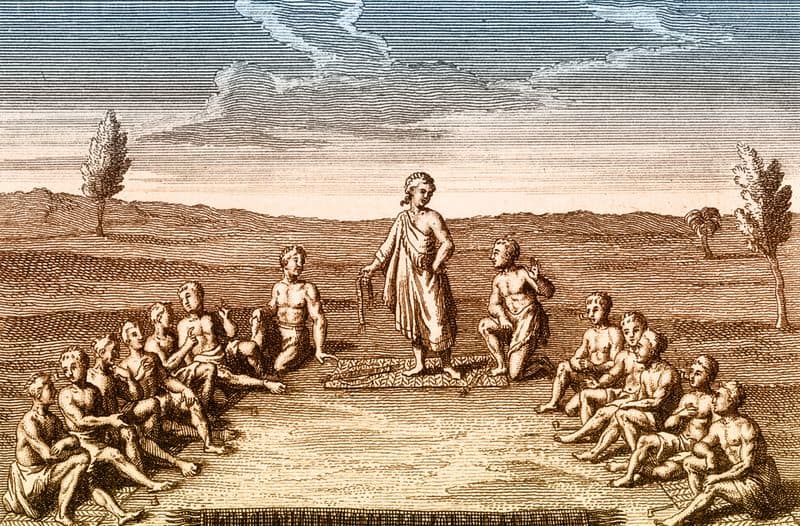

Law and governance were essential to maintaining order in ancient civilizations. By establishing rules and institutions, they ensured stability and justice.
Legal codes, such as Hammurabi’s Code, defined rights and responsibilities, influencing conduct. Governance structures, led by kings or councils, managed resources and directed military efforts.
These systems allowed for organized administration, enabling societies to thrive. While laws often reflected the values of the time, they also laid the foundation for modern legal principles. Governance was about balancing power and responsibility, fostering a sense of community and cooperation.

