Black holes are one of the most mysterious and intriguing phenomena in the universe.
Their immense gravitational pull and enigmatic nature have fascinated scientists and the public alike.
In this blog post, we delve into 12 jaw-dropping facts about black holes that reveal their dark secrets and captivating allure.
From mind-bending physics to cosmic wonders, these facts will expand your understanding and spark your imagination about the universe’s most enigmatic entities.
1. The Singularity’s Infinite Density

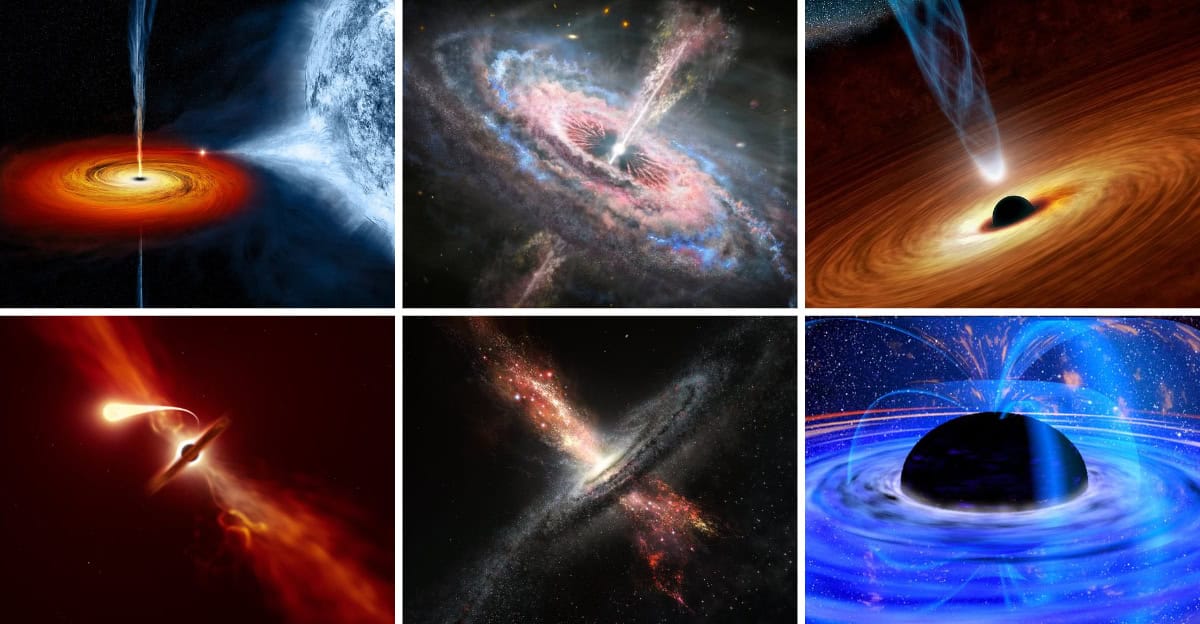
Black holes harbor singularities, points of infinite density where the known laws of physics break down. Imagine a place where mass is squeezed into an infinitely small space.
This singularity is surrounded by the event horizon, a boundary where escape becomes impossible.
Although we cannot observe singularities directly, their existence challenges our understanding of the universe.
The concept intrigues scientists, sparking debates about quantum gravity and the nature of spacetime.
Singularities highlight the limit of our knowledge and the mysteries waiting beyond the veil of our current scientific understanding.
2. Time Dilation Near Black Holes

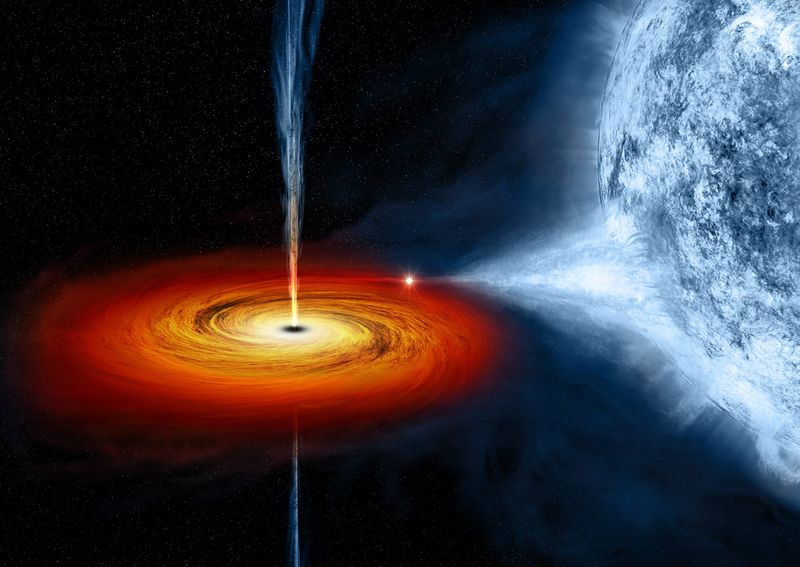
The effects of time dilation near a black hole are profound and perplexing. As an object approaches a black hole, time appears to slow down relative to a distant observer.
This phenomenon is a consequence of general relativity, where immense gravity affects the flow of time.
For an astronaut venturing near a black hole, minutes might pass for them while years elapse for those observing from afar.
This mind-bending effect reveals the interconnectedness of space and time, challenging our perceptions of reality and the universe’s complex fabric.
3. The Largest Black Holes: Supermassive Giants

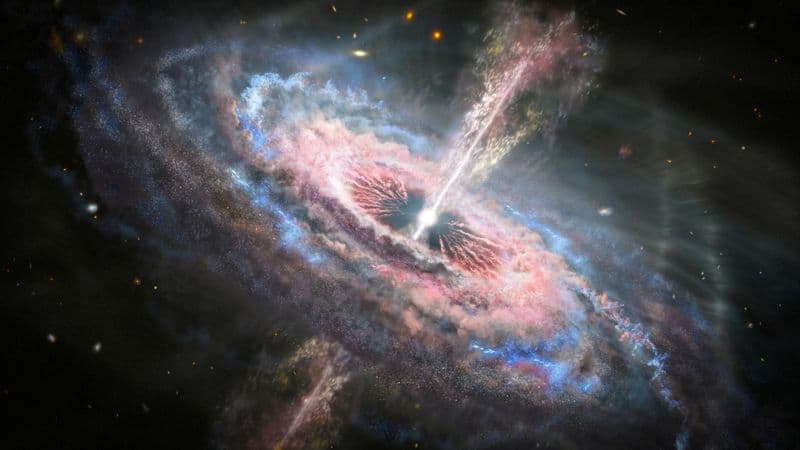
Supermassive black holes reside at the centers of most galaxies, including our Milky Way. These colossal entities can have masses equivalent to billions of suns.
Their origins remain a mystery, with theories suggesting they form from the collapse of massive clouds of gas or the merging of smaller black holes.
Their immense gravitational pull shapes the dynamics of galaxies, influencing the formation of stars and regulating cosmic environments.
Despite their size, supermassive black holes are elusive, hiding their secrets within the heart of galaxies, governing their cosmic domains with unseen power.
4. Hawking Radiation: Black Holes Evaporating
Stephen Hawking’s groundbreaking theory proposed that black holes are not completely black but emit radiation due to quantum effects near the event horizon.
This radiation, known as Hawking radiation, suggests that black holes can eventually evaporate over time.
Though this process is incredibly slow for large black holes, it offers insights into black hole thermodynamics and quantum mechanics.
Hawking radiation challenges the notion of black holes as eternal objects, opening pathways to understanding the interplay between gravity and quantum fields at the universe’s most extreme points.
5. Spaghettification: The Tidal Forces of Doom

The intense gravitational forces near a black hole can lead to a phenomenon known as spaghettification.
As an object approaches a black hole, the differential gravitational pull stretches it into long, thin shapes, like spaghetti.
This dramatic effect results from the difference in gravitational force experienced at different points of the object.
For anything unfortunate enough to venture too close, spaghettification would be the ultimate doom.
This extreme occurrence illustrates the sheer power of black holes and the incredible intensity of their gravitational fields, presenting a cosmic horror that defies imagination.
6. Black Holes as Cosmic Anchors

Black holes are not merely destructive forces; they also play a vital role as cosmic anchors. By anchoring galaxies, they help maintain the structural integrity of the universe.
Their immense gravity holds galaxies together, influencing the motion of stars and the formation of cosmic structures.
Without them, galaxies might lose their cohesion, and the cosmic dance of celestial bodies would be disrupted.
This balancing act highlights their dual nature as both creators and destroyers, playing a fundamental role in the universe’s grand design and cosmic symphony.
7. The Sound of Black Holes

Although sound cannot travel through the vacuum of space, gravitational waves emitted by merging black holes can be converted into sound waves.
Scientists have captured these gravitational waves, translating them into audible frequencies. The result is a cosmic symphony, offering a unique way to “listen” to the universe.
Each merger produces a distinct signal, akin to the sound of a distant bell or drum.
This auditory approach to observing black holes enhances our understanding and appreciation of the universe’s dynamic events, allowing us to experience cosmic phenomena in a novel way.
8. The First Image of a Black Hole
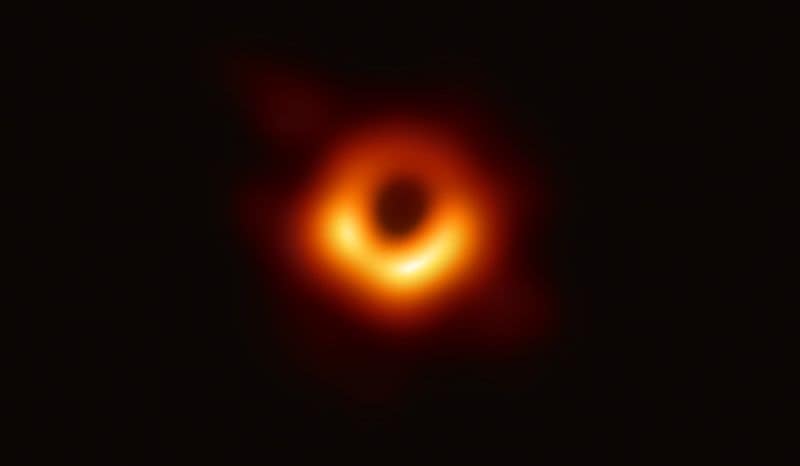

The first image of a black hole was captured in 2019 by the Event Horizon Telescope, a global network of radio observatories.
This groundbreaking achievement unveiled a supermassive black hole in the galaxy M87, revealing its shadow surrounded by a bright ring of accreting material.
The image marked a monumental leap in astrophysics, providing visual evidence of black holes’ existence.
This visual confirmation supports Einstein’s theory of general relativity and offers insights into the behavior of matter and energy in the most extreme environments, pushing the boundaries of scientific exploration.
9. Black Holes and Information Paradox

The black hole information paradox challenges our understanding of fundamental physics.
According to quantum mechanics, information cannot be destroyed, yet black holes seem to erase it.
When matter falls into a black hole, the information it carries appears to vanish beyond the event horizon.
This paradox raises questions about the fate of information and the laws of quantum mechanics.
Scientists are actively exploring potential resolutions, such as holographic principles or new theories of gravity.
The information paradox remains a tantalizing enigma at the intersection of quantum theory and cosmology.
10. Wormholes: Theoretical Pathways Through Space

Wormholes are theoretical passages through space-time, potentially connecting distant regions of the universe.
While often associated with science fiction, they arise from solutions to Einstein’s equations of general relativity.
Black holes are sometimes considered gateways to these exotic structures. Although no observational evidence supports their existence, wormholes captivate the imagination.
They offer intriguing possibilities for faster-than-light travel and new insights into the universe’s geometry.
The concept of wormholes continues to inspire scientific inquiry and speculative exploration, bridging the gap between theoretical physics and cosmic wonder.
11. Primordial Black Holes: Relics of the Early Universe
Primordial black holes are hypothetical remnants from the early universe, possibly formed shortly after the Big Bang. Unlike stellar black holes, they could be as small as an atom yet contain the mass of a mountain.
These ancient entities might contribute to dark matter, influencing the universe’s structure.
Despite their elusive nature, primordial black holes offer insights into the universe’s infancy and the conditions that prevailed.
Understanding them could unravel mysteries about the cosmos’s origins and evolution, providing clues to the nature of dark matter and the universe’s hidden components.
12. The Role of Black Holes in Galaxy Formation

Black holes are pivotal to galaxy formation, acting as seeds around which galaxies coalesce. Their gravity pulls in vast amounts of gas, triggering star formation and shaping galactic development.
Observations suggest that the mass of a galaxy’s central bulge correlates with its central black hole, hinting at a co-evolutionary relationship.
This connection underscores the significance of black holes in the cosmic narrative, influencing the growth and architecture of galaxies.
By understanding their role, we gain insights into the universe’s grand design and the forces sculpting its majestic structures.

