Gladiators, the iconic warriors of ancient Rome, are often seen solely as brutal fighters.
However, there’s much more to their story than meets the eye. These combatants were a complex blend of athletes, entertainers, and even celebrities in their own right.
In this blog post, we delve into 12 surprising facts that reveal the multifaceted world of gladiators, unveiling their roles beyond the arena.
1. Gladiatorial Schools

Gladiators were trained in specialized schools known as ludus.
These schools were run by a lanista, who was responsible for the training and discipline of the gladiators.
Training was intense and focused on developing skills specific to different combat styles. These schools were not just about physical training; they also emphasized strategy and mental toughness.
Gladiators often formed bonds, considering each other comrades-in-arms, which was crucial for their survival. This camaraderie was a key aspect of their daily lives.
2. Women Gladiators

While predominantly male, the ranks of gladiators also included women, known as gladiatrices.
These female fighters faced similar rigorous training and fought in the arenas, drawing large crowds. Though less common, their presence was a testament to the diversity of gladiatorial combat.
They often performed in pairs or small groups. The novelty of female fighters added a unique spectacle to the games, challenging societal norms and earning them a place in Roman history.
Their fights were both a form of entertainment and a statement.
3. Gladiators’ Diet
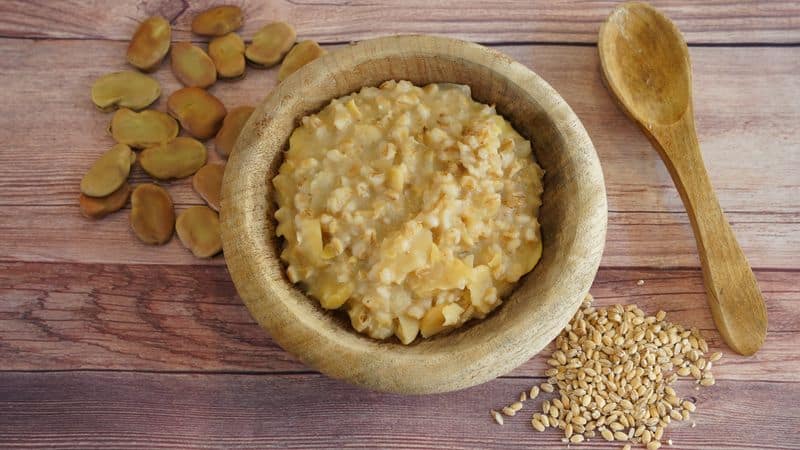

Contrary to popular belief, gladiators followed a vegetarian diet rich in carbs. Their consumption mainly consisted of grains and beans, earning them the nickname ‘barley men.’
This diet helped in building mass and providing sustained energy for combat.
The focus was on maintaining their health and stamina rather than pure muscle strength. They also drank an ash tonic, believed to fortify their bodies.
This unique diet was integral to their physical regimen and contributed to their endurance in the arena.
4. Gladiators as Celebrities

Successful gladiators enjoyed celebrity status akin to modern sports stars. They were admired and cheered by the masses, and their victories were celebrated by all.
Public adoration often translated into lucrative sponsorships and gifts. They were also immortalized in art and poetry.
However, this fame came with its own pressures and expectations.
Gladiators had to constantly prove themselves worthy of their fans’ admiration. This dual life of fame and danger made their existence both glamorous and perilous.
5. The Colosseum’s Role
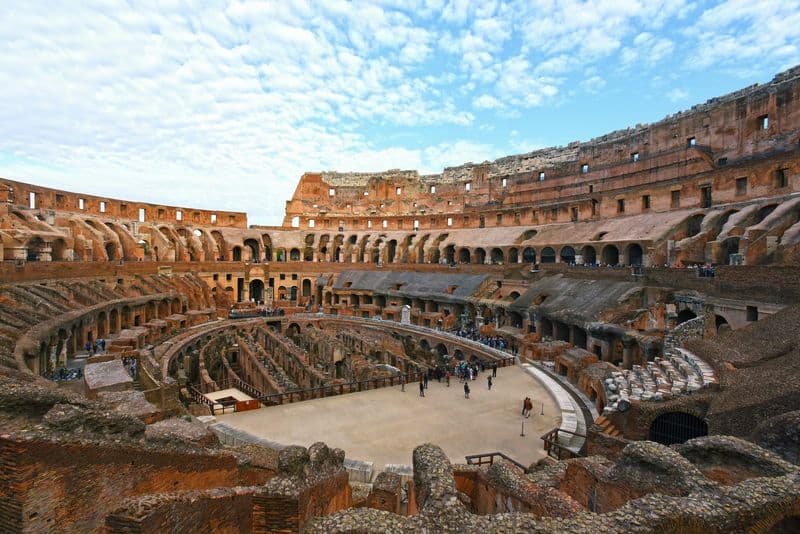

The Colosseum was the grand stage for gladiatorial combats, showcasing the might of Rome. This architectural marvel could hold up to 50,000 spectators, all eager to witness the spectacle.
The arena was designed for various types of games and could even be flooded for mock naval battles. Gladiators fought for glory and survival in this imposing structure.
The Colosseum symbolized the Roman Empire’s power and culture, serving as a testament to the grandeur of ancient Rome. It remains a historical icon today.
6. Social Status of Gladiators

Gladiators came from diverse backgrounds, including slaves, criminals, and volunteers. Despite their origins, successful gladiators could rise in social status, gaining wealth and freedom.
This upward mobility was rare in ancient societies. Their skill in combat earned them respect and admiration from all classes.
However, the path to such recognition was fraught with peril and required immense dedication.
Gladiators often had to navigate complex social dynamics. Their stories reflect the intricate social fabric of ancient Rome.
7. Medical Care for Gladiators

Gladiators received some of the best medical care of their time, often treated by skilled medics.
Given the harshness of their profession, injuries were frequent, and quick recovery was essential.
Medical practitioners used herbs and rudimentary surgical techniques to heal wounds. This care was vital in prolonging gladiators’ careers and ensuring they could return to the arena.
The emphasis on medical treatment highlights the professional care gladiators received, underscoring their value as entertainers and athletes.
8. The Gladiatorial Oath

Upon joining, gladiators took a solemn oath, pledging to endure perilous combat. This oath symbolized their commitment to the life they chose or were thrust into.
It was a binding promise to fight valiantly and accept the dangers that came with it. The oath was both a form of initiation and a psychological preparation for the brutal reality of the arena.
This ritual was a crucial part of a gladiator’s identity, shaping their mindset and camaraderie with fellow fighters.
9. Animal Hunts in Arenas

Beyond human combat, arenas hosted venationes, or wild animal hunts, as part of the entertainment. Gladiators, sometimes specializing as bestiarii, faced a variety of dangerous animals.
These hunts were thrilling spectacles, showcasing bravery and skill. The inclusion of wild beasts added another layer of excitement and danger to the games.
These events demonstrated the gladiators’ versatility and adaptability. The venationes were a testament to the grandeur and diversity of Roman entertainment, captivating audiences from all walks of life.
10. Gladiators’ Impact on Language

The influence of gladiators extended into language, with many terms still used today. Words like ‘arena’ and ‘gladiator’ have roots in these ancient combats.
Gladiatorial games inspired expressions that conveyed struggle and valor. This linguistic legacy highlights the cultural permeation of gladiatorial life.
The terminology associated with gladiators reflected their impact on Roman society. Such language elements have transcended time, continuing to shape modern vocabularies.
This enduring influence underscores the gladiators’ role beyond mere entertainment.
11. Freedom for Gladiators
Gladiators could earn their freedom through exceptional performance, receiving a rudis as a symbol. This wooden sword represented their release from duty.
Freed gladiators often became trainers, leveraging their experience. This path was a beacon of hope for many, driving them to excel in the arena.
The prospect of freedom was a powerful motivator, offering a new lease on life. For many, this opportunity to transition from combatant to free citizen was the ultimate reward after years of struggle.
12. Honoring Fallen Gladiators

Fallen gladiators were honored in elaborate ceremonies, reflecting their status as both entertainers and warriors. These rites involved processions and offerings, acknowledging their bravery.
Such ceremonies underscored the respect they garnered, even in death. The rituals served to commemorate their contributions to Roman culture.
These honors were a poignant reminder of the gladiators’ dual existence—celebrated in life and revered in death. Through these ceremonies, gladiators were immortalized, their legacy etched in the annals of history.

