The Pacific Ring of Fire is a vast and awe-inspiring zone encircling the Pacific Ocean.
Known for its intense seismic and volcanic activity, this region is a powerhouse of geological phenomena.
From towering volcanoes to deep ocean trenches, the Ring of Fire is a dynamic and complex system that captures the imagination of scientists and explorers alike.
Here are 12 incredible facts about this fiery region that are sure to ignite your curiosity.
1. A Volcanic Hotspot
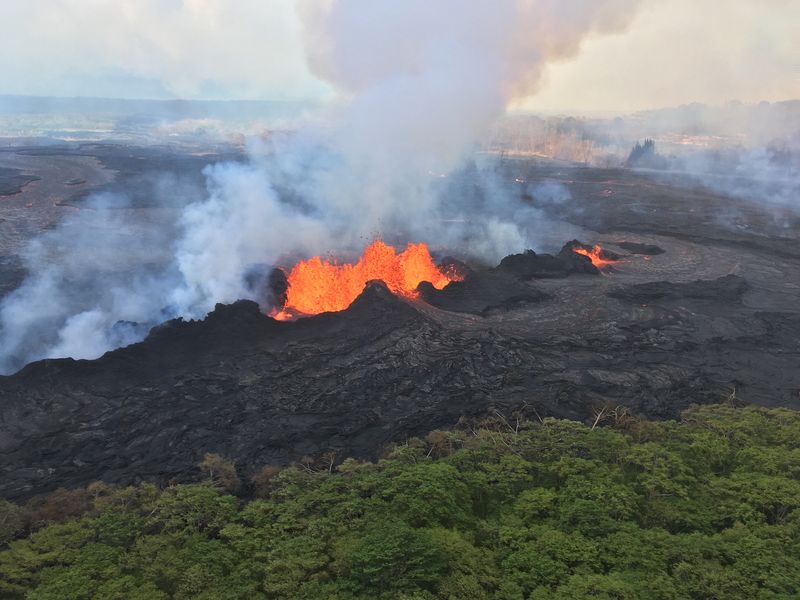

The Pacific Ring of Fire is home to about 75% of the world’s volcanoes. This remarkable fact highlights the immense volcanic activity concentrated in this region.
The tectonic plates beneath the ocean floor are constantly moving, which leads to frequent eruptions.
However, it’s not just the number that astounds, but the sheer power and unpredictability of these eruptions.
Many islands in the Pacific owe their very existence to this fiery activity, constantly reshaping the landscape.
This hotspot of volcanic activity is a testament to the ever-changing nature of our planet.
2. Birthplace of Tsunamis
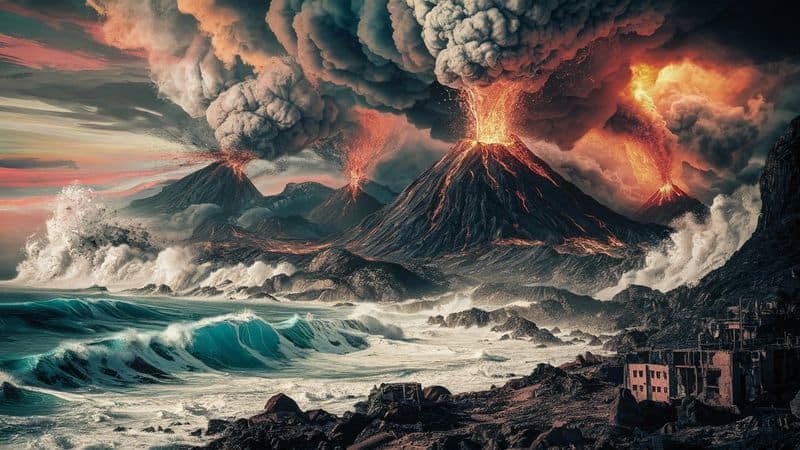

The Ring of Fire is not only known for volcanoes but also for giving birth to tsunamis. These massive waves are often triggered by undersea earthquakes, which are common in this region.
The sudden displacement of water can send towering waves racing across the ocean at terrifying speeds.
Coastal communities have developed sophisticated warning systems to mitigate the impact. Despite these advances, the raw power and unpredictability of tsunamis continue to pose a significant threat.
The Ring of Fire remains a crucial area for research and monitoring to better understand and predict these natural disasters.
3. Earthquake Central
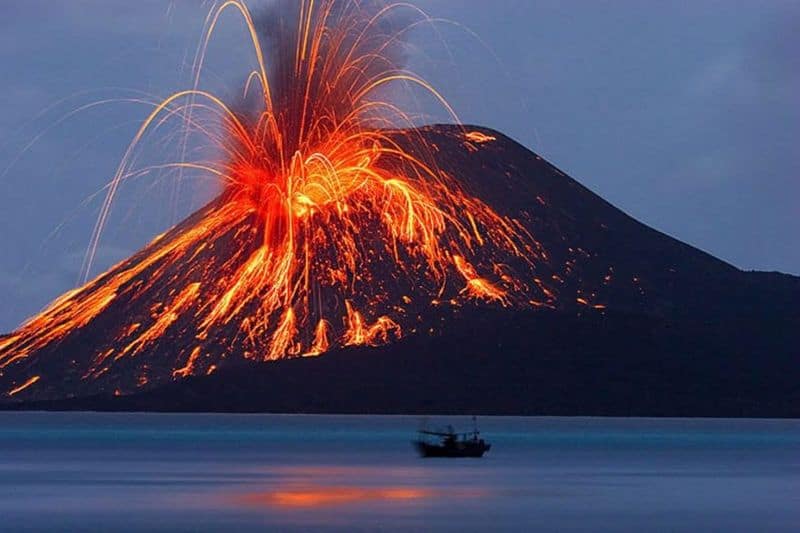

The Pacific Ring of Fire experiences about 90% of the world’s earthquakes.
This staggering statistic underscores the intense seismic activity along the tectonic plate boundaries that define this region. The continuous subduction of plates generates a massive amount of stress, resulting in frequent tremors.
Earthquakes can range from minor shakes to devastating events causing widespread damage.
This relentless seismic activity requires constant vigilance and preparedness from those living within its reach.
Understanding the mechanics of these earthquakes is vital for developing better building practices and resilience strategies.
4. Diverse Ecosystems
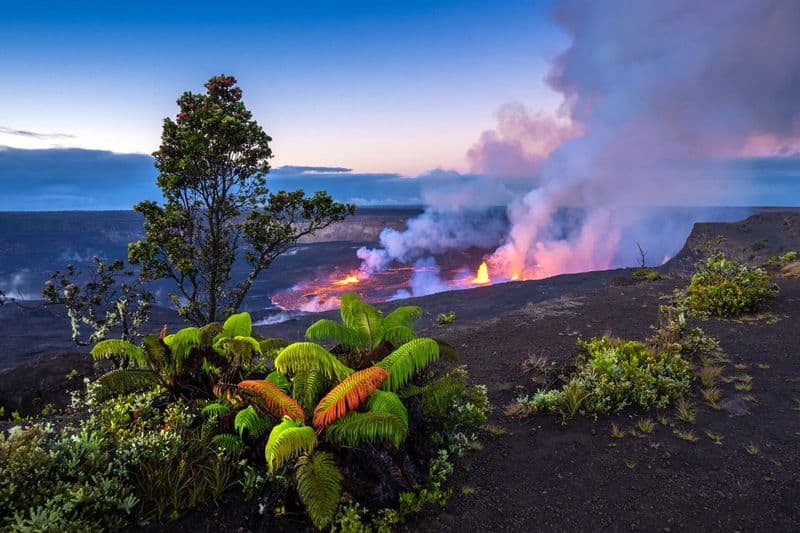

Despite the volatile environment, the Pacific Ring of Fire hosts some of the most diverse ecosystems on the planet. The nutrient-rich volcanic soil supports vibrant plant life, fostering habitats for countless species.
From dense rainforests to vibrant coral reefs, life thrives in the shadow of volcanos. These ecosystems are essential for maintaining ecological balance and providing unique opportunities for scientific study.
The resilience and adaptability of life in these areas offer insights into evolution and survival. Protecting these ecosystems is crucial for preserving biodiversity and understanding natural processes.
5. Home to Supervolcanoes
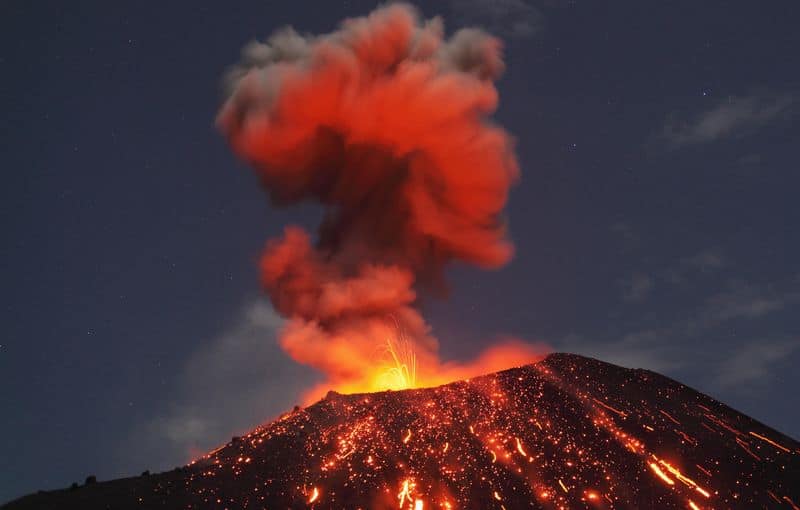

Within the Pacific Ring of Fire lies some of the world’s supervolcanoes. These colossal volcanoes have the potential to produce eruptions thousands of times more destructive than regular volcanic eruptions.
The immense calderas formed by past eruptions are a testament to their devastating power.
While these supervolcanoes remain dormant for thousands of years, the potential for future eruptions is always present. Monitoring these giants is crucial for understanding the risks they pose.
Their presence reminds us of the dynamic nature of Earth’s geology and the need for continued research.
6. The Deepest Ocean Trench
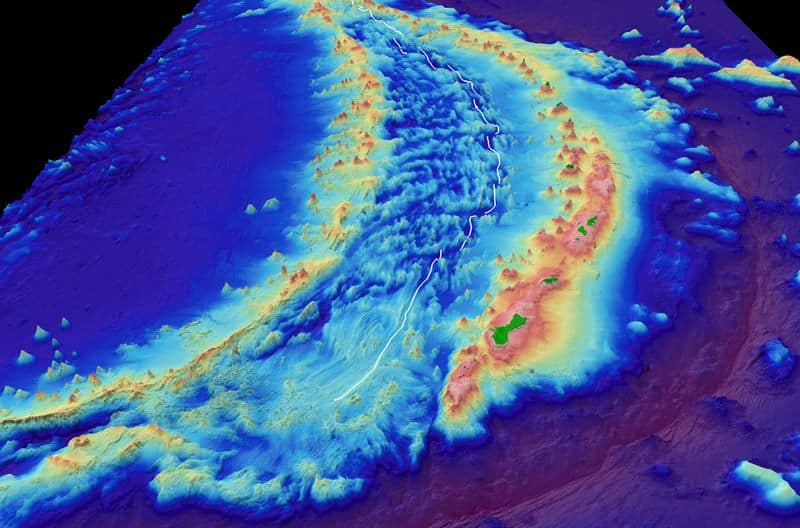
The Mariana Trench, part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, is the deepest oceanic trench known to man. This trench plunges down nearly 36,000 feet, deeper than Mount Everest is tall.
The extreme pressure and darkness create a unique and largely unexplored world. Strange and resilient organisms have adapted to these harsh conditions, providing a glimpse into the extremes of life on Earth.
Exploring the trench is a challenging but rewarding endeavor, offering insights into geology and biology.
The mysteries of the Mariana Trench continue to captivate scientists and explorers alike.
7. Cultural Significance

For many indigenous cultures, the Pacific Ring of Fire holds deep spiritual and cultural significance. Volcanic features are often integral to myths and legends, symbolizing creation, destruction, and renewal.
Rituals and ceremonies are performed to honor these powerful natural forces. This cultural heritage enriches the understanding of human connections to the land.
Preserving these traditions is vital for maintaining cultural diversity and passing knowledge to future generations.
The interplay between culture and nature in the Ring of Fire offers a unique perspective on how humans relate to their environment and adapt to its challenges.
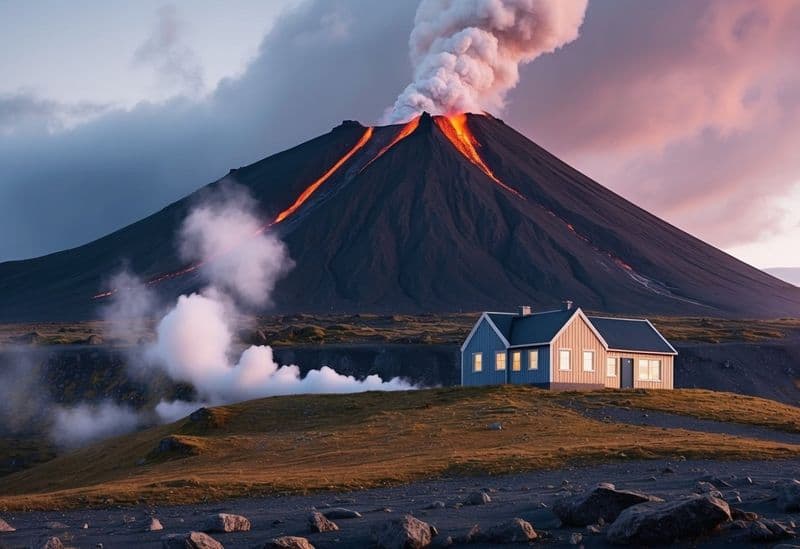
8. Geothermal Energy Potential

The Pacific Ring of Fire is a potential powerhouse for geothermal energy.
This renewable energy source harnesses heat from the Earth’s core, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
Countries within the Ring of Fire, such as Iceland and New Zealand, are leading the way in geothermal energy production.
This technology reduces reliance on non-renewable resources and lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
The vast geothermal potential in this region provides an opportunity for energy diversification.
Investing in geothermal energy can help combat climate change and promote energy security.
9. Unique Geological Features
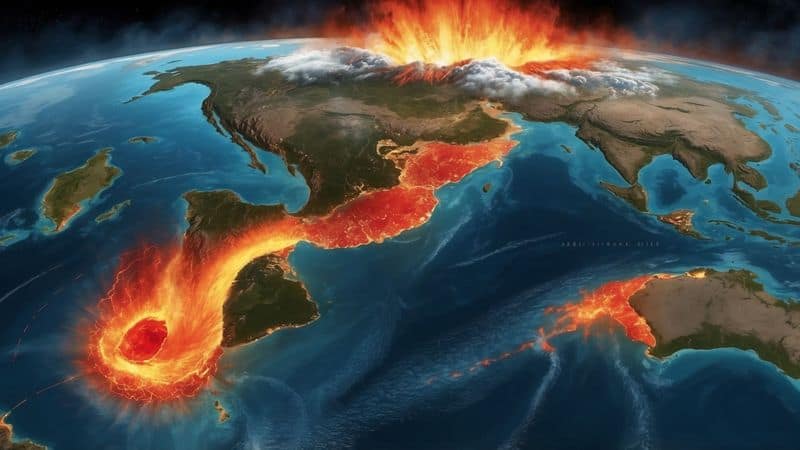

The Pacific Ring of Fire is adorned with unique geological features that captivate geologists. From jagged volcanic peaks to expansive lava fields, these landscapes tell the story of Earth’s dynamic history.
Each feature holds clues about past geological events and processes. Studying these formations helps scientists understand plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and Earth’s geological evolution.
These features also attract tourists, offering breathtaking views and adventurous exploration opportunities.
Preserving these natural wonders is essential for scientific research and environmental education.
The Ring of Fire stands as a living laboratory of Earth’s geological marvels.
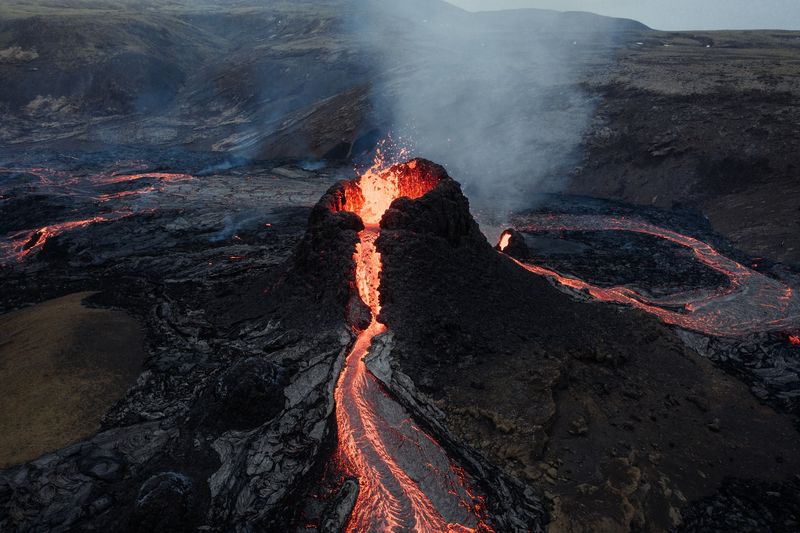
10. The Fire Underwater
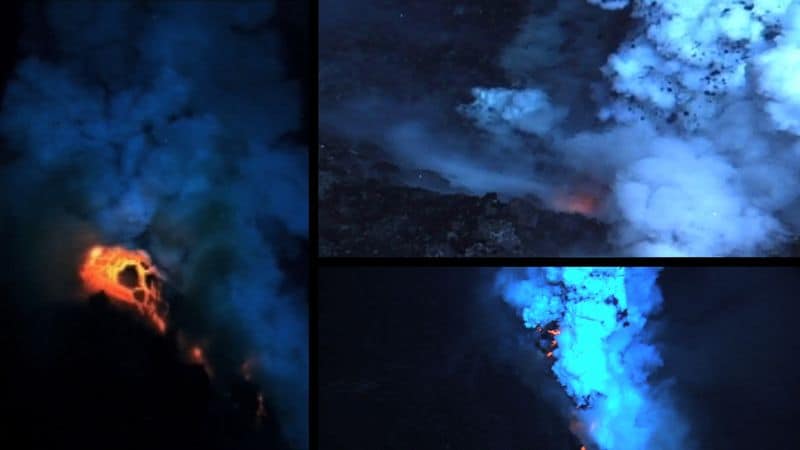

Beneath the ocean’s surface, the Pacific Ring of Fire is alive with underwater volcanic activity. These submarine volcanoes contribute to seafloor spreading and the creation of new land.
The intense heat and pressure cause spectacular eruptions, visible as steam and ash clouds on the ocean’s surface.
Despite their remote location, these eruptions impact ocean chemistry and marine life. Understanding submarine volcanic activity is crucial for studying ocean dynamics and plate movement.
This hidden fire beneath the waves reminds us of the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the mysteries that lie beneath the sea.
11. Tectonic Plate Interactions
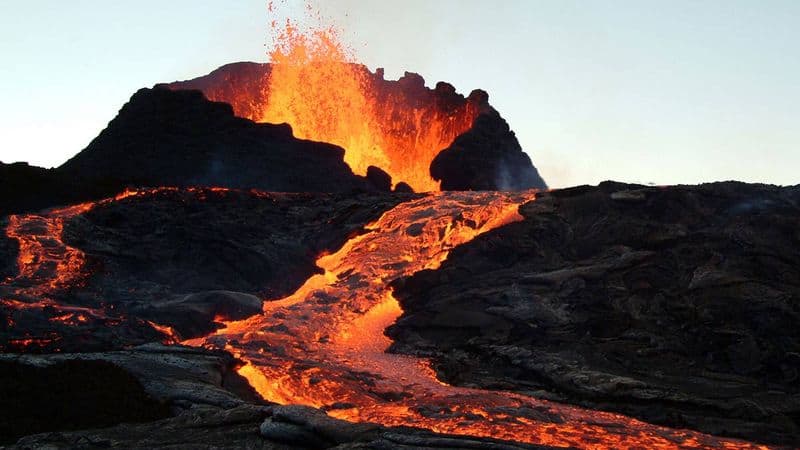

The Pacific Ring of Fire is a result of complex tectonic plate interactions.
The movement and collision of plates drive volcanic and seismic activity in this region. Subduction zones, where one plate slides beneath another, are hotspots for earthquakes and volcanism.
These interactions shape the landscape and influence global geological processes.
Understanding plate tectonics is crucial for predicting natural disasters and mitigating their impact.
The Ring of Fire serves as a natural laboratory for studying these interactions.
Advances in technology and research continue to unravel the mysteries of Earth’s tectonic behavior.
12. A Window into Earth’s Interior
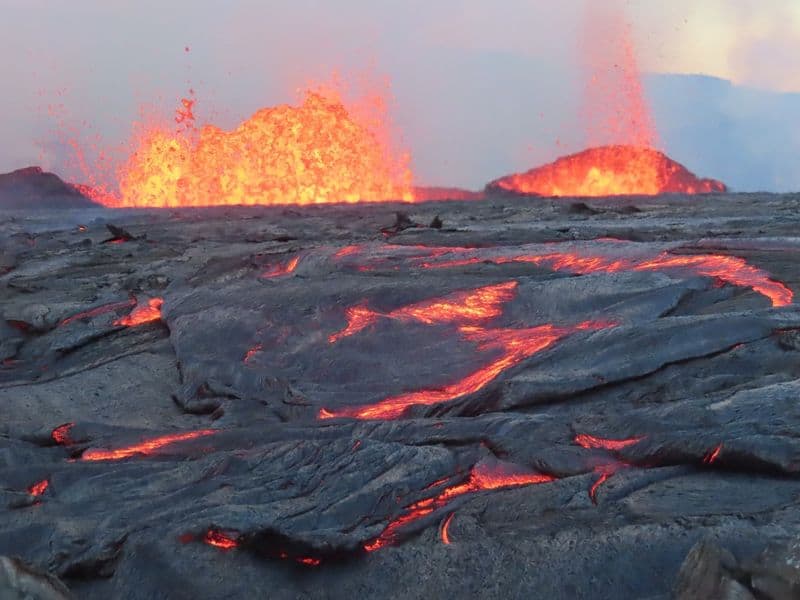

The Pacific Ring of Fire offers a unique window into the Earth’s interior. Volcanic eruptions bring magma from deep within the Earth to the surface, providing a glimpse into the planet’s inner workings.
Analyzing the composition of volcanic rocks helps scientists learn about the Earth’s mantle and core. This knowledge is vital for understanding the planet’s formation and evolution.
The Ring of Fire plays a crucial role in advancing geological science and educating the public about Earth’s dynamic nature.
Studying this fiery region enhances our understanding of the planet we call home.

