Trees are not just towering giants that provide shade and oxygen. They hold secrets and wonders that are often overlooked.
From ancient myths to modern discoveries, trees continue to amaze us with their unique features and roles in our ecosystem.
This blog delves into twelve intriguing facts about trees that highlight their incredible nature and importance.
1. Trees Communicate Underground

Did you know that trees have their own form of communication? Underground, tree roots are connected by a network of fungi known as the ‘Wood Wide Web.’
This fascinating system allows trees to exchange nutrients, water, and even chemical signals. It’s like their very own internet!
Through this underground network, trees can warn each other of dangers such as pests or diseases.
They can also help out their neighbors, sharing excess nutrients. This hidden world beneath our feet plays a crucial role in forest health and resilience. Truly, trees are more connected than we realize.
2. Oldest Known Tree
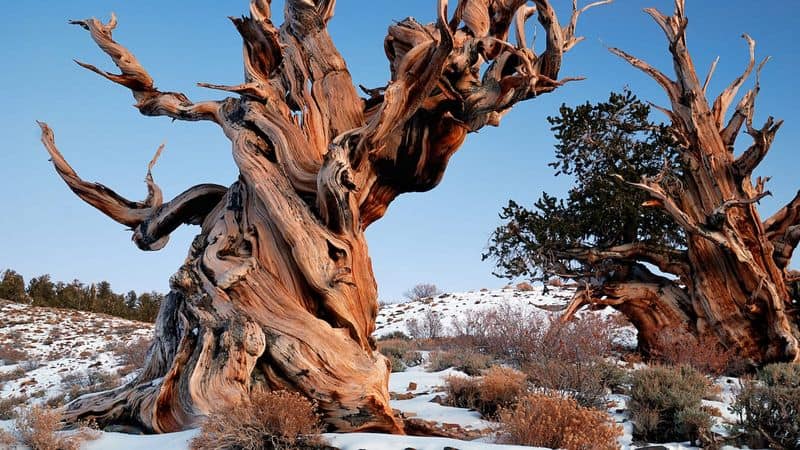

The oldest known living tree is a remarkable bristlecone pine named Methuselah, located in California’s White Mountains.
At over 4,800 years old, it has witnessed millennia of history. Imagine the stories it could tell!
This ancient tree has survived natural disasters, climate changes, and human interference. Its twisted branches and gnarled trunk stand as a testament to resilience and longevity.
However, its exact location is kept secret to protect it from vandalism. Methuselah’s age and endurance make it a true natural wonder that continues to inspire awe.
3. Trees Can Save Lives
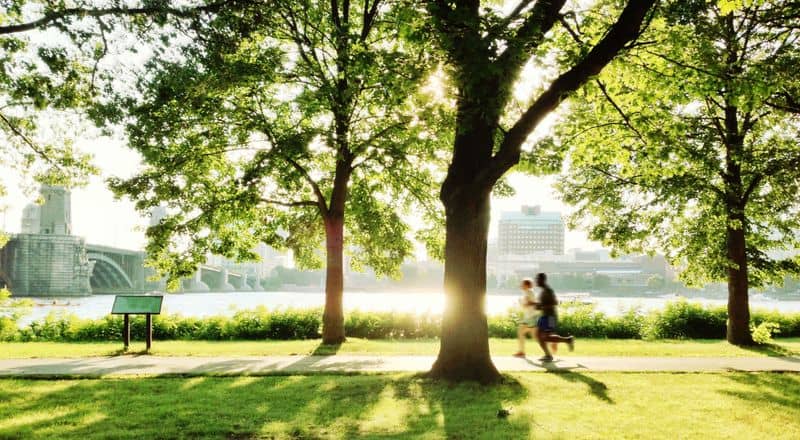

Trees play a vital role in our urban environments, providing shade and cooling the air.
This can have life-saving effects, especially during heatwaves. Research shows that areas with more trees can be significantly cooler than areas without.
This natural cooling effect helps reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses and deaths.
By lowering air temperature, trees can also reduce the need for air conditioning, saving energy and cutting costs.
Planting and preserving trees in cities is more than just beautification; it’s an essential part of urban planning for health and sustainability.
4. Trees and Carbon Storage

Trees are incredible carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it as they grow.
This process not only helps mitigate climate change but also provides us with oxygen.
Different species of trees have varying capacities for carbon storage, with some able to store more than others.
Forest conservation and reforestation are vital strategies in combating global warming.
Supporting these efforts can have a profound impact on our planet’s future. Trees truly are nature’s air purifiers, working tirelessly to keep our environment balanced.
5. The Tallest Tree
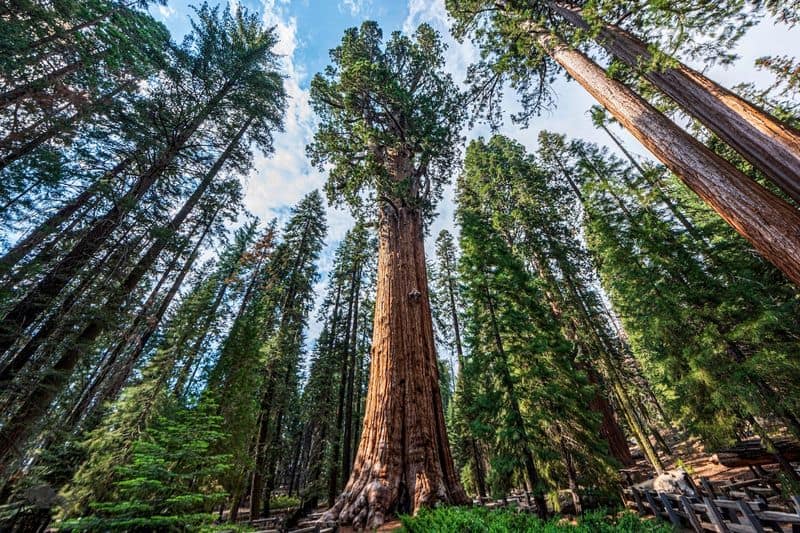

Standing tall at 379.7 feet, Hyperion is the world’s tallest known tree. Located in California’s Redwood National Park, this coast redwood was discovered in 2006. Its towering presence is awe-inspiring!
The exact location of Hyperion is kept secret to protect it from damage.
Its towering height is a testament to the incredible growth potential of redwoods.
These trees can live for over 2,000 years, reaching staggering heights and creating unique ecosystems high in their canopies.
Hyperion’s majesty reminds us of the grandeur and mystery of nature.
6. Trees and Water Regulation
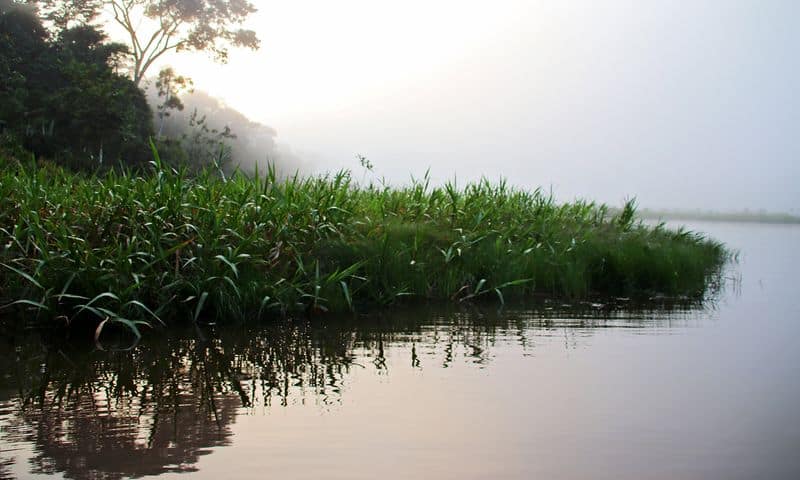

Trees play a crucial role in regulating water cycles. Through a process called transpiration, they release water vapor into the atmosphere, contributing to cloud formation and precipitation.
Forests act like giant sponges, absorbing rainfall and slowly releasing it into rivers and streams.
This helps prevent floods and maintain water quality. Deforestation can disrupt these vital processes, leading to water scarcity and increased flooding.
By preserving and restoring forests, we support natural water regulation and sustain vital resources for both wildlife and human communities.
7. Unique Tree Shapes
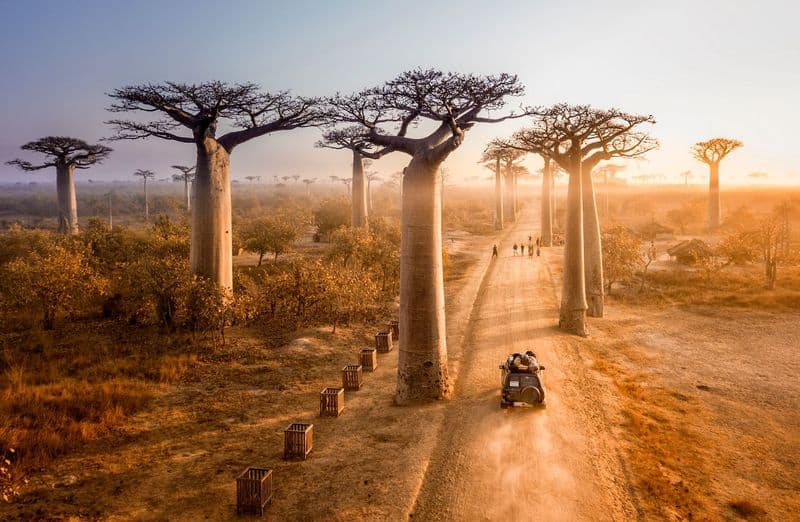

Some trees are known for their unique and bizarre shapes. The baobab tree, for example, has a trunk that resembles a giant bottle, storing water for dry seasons.
Meanwhile, the dragon tree has an umbrella-like canopy that’s both alien and beautiful.
These unusual shapes are not just for show. They serve specific ecological purposes, such as water conservation or sunlight capture.
Exploring these unique trees reveals the creativity and adaptability of nature. Each tree’s shape is a response to its environment, showcasing the diverse strategies of survival.
8. Trees and Biodiversity
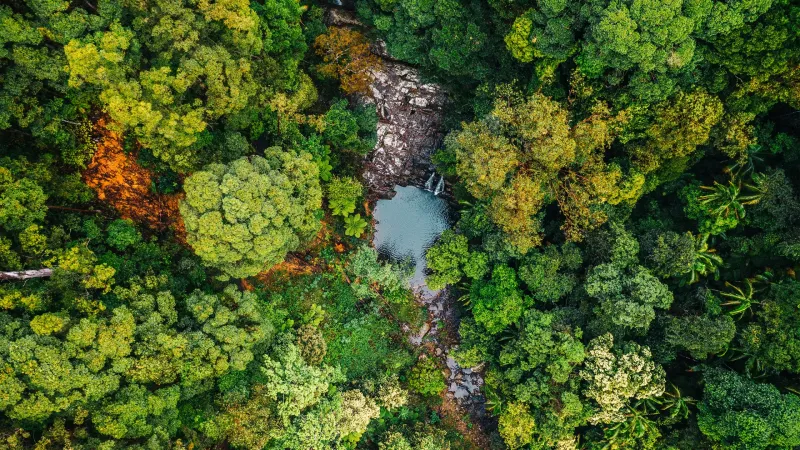

Forests are biodiversity hotspots, home to more than 80% of the world’s terrestrial species. Trees provide essential habitats and resources for countless creatures, from insects to large mammals.
The complex structure of tree canopies supports diverse ecosystems, facilitating interactions among species.
Protecting forests is crucial to maintaining global biodiversity. Each tree can be a mini-ecosystem, hosting unique life forms.
By conserving trees, we preserve the intricate web of life that makes our planet vibrant and resilient.
9. Trees in Mythology
Throughout history, trees have played significant roles in mythology and folklore.
The Norse mythology tree, Yggdrasil, was believed to connect the heavens, earth, and underworld, serving as the axis of the world.
Many cultures have revered trees as sacred symbols of life and knowledge.
From ancient druidic practices to modern spiritual beliefs, trees have inspired awe and reverence.
These mythical connections reflect humanity’s deep-rooted relationship with trees and nature.
Understanding these stories provides insight into cultural values and the timeless significance of trees.
10. Fruit Trees and Evolution

Fruit trees have played a crucial role in the evolution of both plants and animals.
By producing delicious fruits, these trees attract animals that help disperse their seeds. This symbiotic relationship has shaped the evolution of countless species.
The diversity of fruit shapes, colors, and tastes reflects the adaptability and innovation of nature.
From apples to bananas, fruit trees have influenced human agriculture and diets.
Understanding this evolutionary success story highlights the interconnectedness of life and the importance of preserving diverse fruit species for future generations.
11. Trees and Medicine

Many trees have medicinal properties that have been used for centuries.
The bark of the willow tree, for example, contains salicin, a precursor to aspirin. Cinchona tree bark is the source of quinine, a treatment for malaria.
These natural remedies highlight the importance of trees in traditional and modern medicine.
Researchers continue to explore forests for new medical discoveries, emphasizing the need to protect these vital resources.
Trees offer a wealth of healing potential, reminding us of the profound connection between nature and human health.
12. Trees and Art

Trees have long been a source of inspiration for artists, featuring prominently in paintings, sculptures, and literature.
Their beauty, majesty, and symbolism have captivated human imagination for centuries.
Artists like Vincent van Gogh and Claude Monet have immortalized trees in their work, highlighting the deep emotional and aesthetic connections we have with these natural wonders.
Trees continue to inspire creativity and reflection, serving as muses for new generations.
Their presence in art underscores the timeless and universal appeal of trees, bridging cultures and eras.

